Does Acupuncture Really Work? A Scientific Guide to Its Benefits
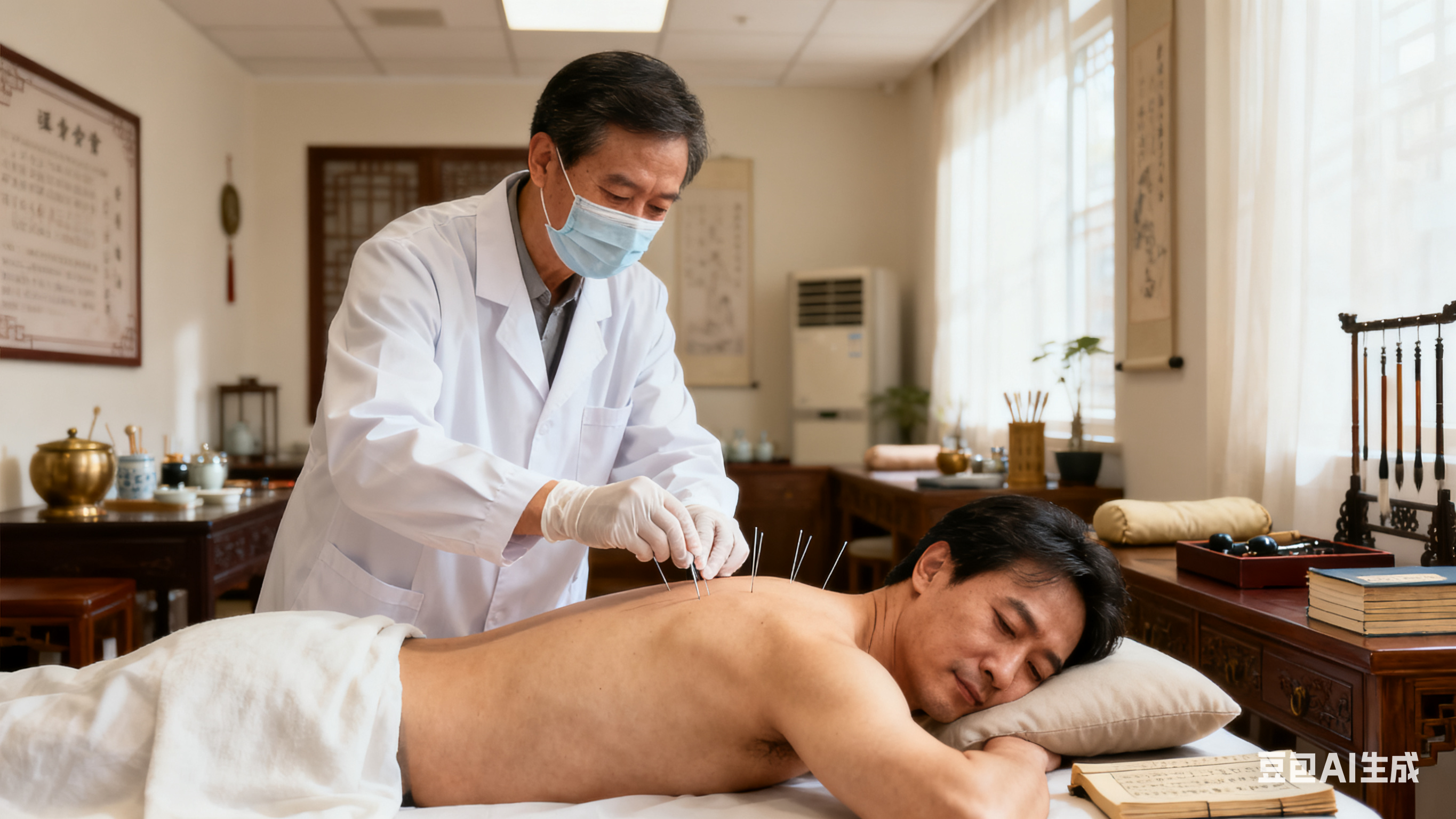
Does Acupuncture Really Work? A Scientific Guide to Its Benefits For millennia, acupuncture has been a cornerstone of Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM), sparking global curiosity about its efficacy. But does it truly work? Modern science and clinical evidence suggest it does—here’s why. Historical Roots and Modern Validation Originating in China over 2,500 years ago, acupuncture involves inserting fine needles into specific acupoints along energy pathways called meridians. While rooted in ancient philosophy, today’s research highlights its physiological impacts. For example, studies show acupuncture triggers the release of endorphins (natural painkillers) and modulates the nervous system to reduce inflammation . The World Health Organization (WHO) endorses acupuncture for treating 77 conditions, including chronic pain, migraines, and digestive disorders . Scientific Mechanisms Explained
- Pain Relief: Acupuncture stimulates nerves, blocking pain signals and promoting muscle relaxation. This is particularly effective for back pain, osteoarthritis, and post-surgical discomfort .
- Immune and Hormonal Balance: By targeting acupoints, it enhances immune function and regulates hormones like cortisol (stress) and serotonin (mood) .
- Mental Health: Research links acupuncture to reduced anxiety and improved sleep by calming the sympathetic nervous system nccih.nih.gov.